Related Topics
Quakers: The Society of Friends
According to an old Quaker joke, the Holy Trinity consists of the fatherhood of God, the brotherhood of man, and the neighborhood of Philadelphia.
Quakers: William Penn
Although Ben Franklin gets more ink lately, William Penn deserves at least equal rank among the most remarkable men who ever lived.
The Proprietorship of West Jersey
The southern half of New Jersey was William Penn's first venture in real estate. It undoubtedly gave him bigger ideas.
Historical Motor Excursion North of Philadelphia
The narrow waist of New Jersey was the upper border of William Penn's vast land holdings, and the outer edge of Quaker influence. In 1776-77, Lord Howe made this strip the main highway of his attempt to subjugate the Colonies.
New Jersey (State of)
 The Garden State really has two different states of mind. The motto is Liberty and Prosperity.
The Garden State really has two different states of mind. The motto is Liberty and Prosperity.
Shaping the Constitution in Philadelphia
After Independence, the weakness of the Federal government dismayed a band of ardent patriots, so under Washington's leadership a stronger Constitution was written. Almost immediately, comrades discovered they had wanted the same thing for different reasons, so during the formative period they struggled to reshape future directions . Moving the Capitol from Philadelphia to the Potomac proved curiously central to all this.
Right Angle Club 2009
The 2009 proceedings of the Right Angle Club of Philadelphia, beginning with the farewell address of the outgoing president, John W. Nixon, and sadly concluding with memorials to two departed members, Fred Etherington and Harry Bishop.
Popular Passages
New topic 2013-02-05 15:24:06 description
Line Dividing East from West Jersey

|
| William Penn |
At this point William Penn entered the picture as one of three Quaker trustees for Byllinge, who had gambling debts. A tenth of this share was given to John Fenwick, the 1675 settler of Salem, to settle his part of the disputes with Byllinge; the rest of it constituted what was to become the oldest American stockholder corporation, The Proprietors of West Jersey. The arrangement up to this point was firmly settled for the southern half of New Jersey by a Quintipartite Deed of July 12, 1676, , signed by the three Quaker trustees plus Byllinge and Fenwick. Aside from establishing the Proprietorship, the main point of this deed was the separation of West Jersey from East Jersey (the Carteret part) by a North-South line which still persists as the upper border of Burlington County. The right to govern this land was fully restored in 1680 by a Confirmatory Grant from James, probably after considerable lobbying in London by William Penn.
Presumably in pursuit of this final confirmation, Penn had negotiated a hundred-page agreement with prospective settlers which outlined his plans for governing, called the Concessions and Agreements of March 14, 1677, . Although its original purpose was mainly a real estate marketing tool, this landmark document seems not only to have persuaded the Duke of York but so shaped the thinking of the English colonies that many of its features are readily recognized in the American Constitution of 1787.
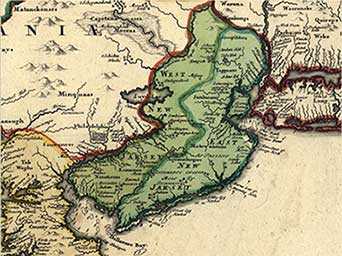
|
| The line dividing West and East NJ |
The land mass between the North and South Rivers (Hudson and Delaware) only came completely and legally into the hands of Quakers in 1681. At that time Carteret's widow, Lady Elizabeth, sold the northern half (East Jersey) to twelve Quaker proprietors, while the southern half (West Jersey) was already held by thirty-two other Quaker proprietors under the effective leadership of William Penn. It is somewhat uncertain who orchestrated this final consolidation, but there is a strong presumption that it was Penn. Since the main purpose of these business proprietorships was to sell land to immigrants, it was vital to minimize land disputes with accurate records and accurate surveying. With a history behind them of fifteen years of bickering, everybody concerned was surely ready for some peaceful organization. Both groups of proprietors, East and West, found it useful to delegate authority to a council of nine executive proprietors, whose main agent under the circumstances was logically the Surveyor General. For the next three hundred years, the surveyor generals were the men running things in New Jersey. The right of the Proprietors to govern was revoked by Queen Anne in 1702, but their land rights remain undisturbed to the present day, notwithstanding the intervening transfer of national power to the United States of America in 1776-83. Underneath all of this hustling and arranging, with exquisite attention to details, seems to be found the hand of William Penn. Almost immediately after New Jersey was packaged and delivered, King Charles paid off his family debt by turning over the far larger combined land mass of Pennsylvania and Delaware to William Penn, urging him to make himself a vassal king in the process. The Quaker instantly declined such a thing, but the power continues to reside in the final Royal Charter. It's only a conjecture, but it might help explain the strange acquaintance between a dissolute king and an abstemious Quaker to notice that the New Jersey tour de force astoundingly demonstrates how Penn was a man who really could be trusted to get complicated things done with dispatch.
Today, for practical purposes it all amounts to a company named Taylor, Wiseman, and Taylor; but we are getting a little ahead of ourselves. To go back to 1684 a surveyed line was clearly needed between the two proprietorships, as declared by the following resolution:
"Award we do hereby declare, that [the line] shall run from ye north side of ye mouth or Inlet of ye beach of little Egg Harbor north northwest and fifty minutes more westerly according to natural position and not according to ye magnet whose variation is nine degrees westward."
To clarify those quaint words, the survey was not to make the mistake made in the layout of Philadelphia, whose streets had intended to be true north and south but by using Magnetic North are actually twelve degrees off from that. Another important point is probably unclear to modern readers, who know the town of Egg Harbor on the mainland of Barnegat Bay but are largely unaware that the "beach of Egg Harbor" was what we now call Long Beach Island, on the east side of Barnegat Bay. The southern anchor of The Line was in what we now call Beach Haven, on the north side of the inlet, although beach erosion has put the southern anchor about two miles out to sea, locating a temporary marker in Beach Haven. Hardly anyone seems to be aware of it, but reread the sentence and observe the meaning is actually quite clear. The intent of the northern end of The Line (? the Delaware Water Gap ?) is buried in the obscurity of compass markings, but comes out slightly above Trenton on the Delaware River, extending beyond the river into Pennsylvania until it reached the river again in a crook on the far side of the Delaware Water Gap. Word of mouth has it that William Penn wanted to have both sides of the river although this triangle of Pennsylvania was eventually surrendered. It seems fair to say, the line was roughly intended to run from the Beach Haven ocean inlet to the Delaware Water Gap.

|
| John, Lord Berkeley |
For its time, the survey of The Line was also a significant engineering achievement. The general plan was to lay out the course of the line in the wilderness until it hit a big boulder or anything else that was large and heavy. This became a marker along a line of 150 markers which could be used for local surveys and boundaries. After several less accurate attempts, the West/East line was surveyed by John Lawrence in 1743 and stands as the Official Province Division Line. A few years ago, a group of volunteers tried to locate all of the original markers and found 55 of them. The historical project took ten years.
All of the deeds of property in the State of New Jersey still depend on the original survey and the meticulous notes kept by the Surveyors General of these two Quaker organizations, without whose private records every title to every property would be clouded. With the passage of time, and especially the warfare of the Revolution, other copies of the surveys have disappeared. So, without the need to get ugly about it, these soft-spoken courteous folks retain a form of power it would be hard to match with sticks and stones, guns, threats or legalisms -- the only surviving record of everyone's title to his land. There is little reason to inquire further why these Proprietorships durably survived the revolution which overthrew King George III, and why no one has seen fit to enter the serious challenge to their claim of owning the whole state except for what they had already specifically sold.
Let's go back to a point made earlier. In all the complexities of the English Royal Court and uncertainties of uncharted wilderness, how did a little band of Quakers find themselves with uncontested ownership of a whole American colony? Some of the chaos of the age probably helped. King Charles unleashed his brother's armies in 1664. Also in 1664, Parliament passed the Second Conventicle Act, which provided that not more than five persons were permitted to worship together otherwise than according to the established ritual of the Anglican Church of England. This act might be described as an improvement on the First Conventicle Act of Queen Elizabeth, which provided that no one at all could so worship. However, this prohibition was so extreme it was ignored, whereas the Second Conventicle probably had some popular support. It thus can be imagined why Quakers were suddenly interested in leaving England, and not hard to understand how young William Penn was propelled into leadership by successfully overturning that Act in the Haymarket Case. Penn was both the defendant in the case and the defense lawyer, inventing the common law principle of jury nullification that has so confounded tyranny ever since. To go on with events current at the time, the Great Plague took place in 1665, making London an undesirable place for anybody to live. And finally, George Fox, the founder of Quakerism, took a journey to the new world in 1672, noting that the place now called Burlington, New Jersey was "a bravest country". Taken altogether, it is not hard to suspect this group of fairly wealthy, fairly well-educated people developed a collective resolve to buy up the pieces, assemble the parcel, and go away to live on it. Their organization into monthly local meetings, quarterly regional meetings, and annual national meetings was surely great assistance. From what we know of the broader vision of William Penn, it is fair to speculate his enthusiasm for this communications network first suggested by George Fox, or at least he's having a pretty quick recognition how it would assist the emigration venture.

|
| George Carteret |
George Carteret's widow was the last to sell out her land parcel to the East Jersey Proprietors, presumably drawn from the 1400 immigrants who had arrived in Burlington on five or six ships between 1678 and 1681. In particular, the ship Kent sailed from the Thames in 1677, bearing 230 Quakers, half from Yorkshire, the other half from London settling further south in West Jersey. Before that, Lord Berkeley had sold his half for a thousand pounds to John Fenwick and Edward Billynge, who arrived in Salem on the ship Griffin in 1674. These two soon fell out, with Fenwick taking a tenth of the land and settling around Salem. Billynge got into unspecified difficulties, probably gambling, and turned his property over to his three main creditors, William Penn, Gawen Lawrie, and Nicholas Lucas, who assembled the Proprietorship of West Jersey. Penn's remarkable talent for leadership again emerged in his statement of "Concessions and Agreements" with the Indians and new inhabitants. In another place, we discuss the reasons for thinking this document created the effective basis of the U.S. Constitution. By infusing it with the unspoken word of compromise, Penn created the main model explaining why the ratification of the Constitution remains the only time in history when thirteen independent nations voluntarily gave up sovereignty for the purpose of creating a larger vision -- which then held together for two centuries. But the voluntary union of East and West Jersey certainly has a claim to being earlier, although its claim to sovereignty is weaker.
Perhaps so, but since their interest in power was weaker, their achievement in peaceful negotiation with a secretly Catholic King was surely much greater. If some small group of religious dissidents should today emerge as having quietly and systematically bought up an entire state, however legally, the word conspiracy would be on every tongue. In this case, however, the reaction was peaceful consensus.
Originally published: Wednesday, August 20, 2008; most-recently modified: Wednesday, August 14, 2019